articles in 2025
all / 2026 / 2025 / 2024 / 2023 / 2022 / 2021 / 2020 / 2019 / 2018 / 2017 / 2016 / 2015 / 2014 / 2013 / 2012 / 2011 / 2010 / 2009 / 2008 / 2007 / 2006 / 2005 / 2004 / 2003 / 2002 / 2001 / 2000 / 1999 / 1998 / 1997 / 1996 / 1995 / 1994 / 1993
-
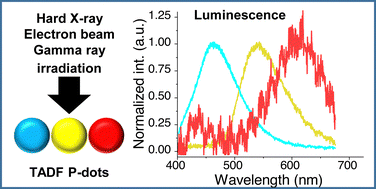 Color variation in radio-luminescence of P-dots doped with thermally activated delayed fluorescence moleculesZheming Su, Hieu Thi Minh Nguyen, Zuoyue Liu, Daiki Asanuma, Minoru Yamaji, Masanori Koshimizu, Hajime Shigemitsu, Sachiko Tojo, Tadashi Mori, Toshiyuki Kida, Guillem Pratx*, Mamoru Fujitsuka*, and Yasuko Osakada*Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2025, 27, 7605–7610.
Color variation in radio-luminescence of P-dots doped with thermally activated delayed fluorescence moleculesZheming Su, Hieu Thi Minh Nguyen, Zuoyue Liu, Daiki Asanuma, Minoru Yamaji, Masanori Koshimizu, Hajime Shigemitsu, Sachiko Tojo, Tadashi Mori, Toshiyuki Kida, Guillem Pratx*, Mamoru Fujitsuka*, and Yasuko Osakada*Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2025, 27, 7605–7610.Thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) materials possess exceptional photophysical properties. Organic scintillators utilizing TADF materials have shown great promise for applications requiring efficient radio-luminescence, owing to their high quantum efficiency and tunable emission properties. Previous studies demonstrated that polymer dots (P-dots) doped with TADF materials exhibit radio-luminescence under hard X-ray and electron beam excitation. However, the TADF materials used in these experiments were limited to limited color options, restricting their utility and hindering the exploration of multicolor radio-luminescence necessary for advanced applications. In this study, we successfully achieved multicolor radio-luminescence-blue, yellow, and red-by developing P-dots doped with TADF materials that emit across the visible spectrum. This breakthrough was demonstrated under excitation by hard X-rays, gamma rays, and electron beams. The ability to realize multicolor radio-luminescence is crucial, as it enables enhanced spatial and spectral resolution, which is vital for applications such as high-precision bio-imaging and multimodal sensing.
@article{su2025color, title = {Color variation in radio-luminescence of P-dots doped with thermally activated delayed fluorescence molecules}, author = {Su, Zheming and Nguyen, Hieu Thi Minh and Liu, Zuoyue and Asanuma, Daiki and Yamaji, Minoru and Koshimizu, Masanori and Shigemitsu, Hajime and Tojo, Sachiko and Mori, Tadashi and Kida, Toshiyuki and Pratx, Guillem and Fujitsuka, Mamoru and Osakada, Yasuko}, journal = {Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.}, volume = {27}, number = {15}, pages = {7605--7610}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Royal Society of Chemistry}, doi = {10.1039/d5cp00410a}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1039/d5cp00410a}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {paper}, } -
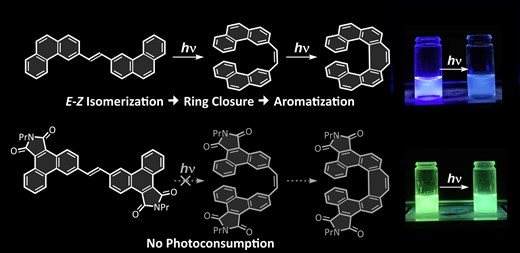 Highly emissive and robust diarylethene fluorophore incorporating imide-fused phenanthryl moietiesKeito Nose, Minoru Yamaji, Tadashi Mori, Fumito Tani, Kenta Goto, and Hideki Okamoto*Chem. Lett., 2025, 54, upaf091.
Highly emissive and robust diarylethene fluorophore incorporating imide-fused phenanthryl moietiesKeito Nose, Minoru Yamaji, Tadashi Mori, Fumito Tani, Kenta Goto, and Hideki Okamoto*Chem. Lett., 2025, 54, upaf091.The fluorescence properties and photostabilities of (E)-diarylethenes (DPEs), featuring two 3-phenanthryl moieties, were investigated. Pristine (E)-di-1,2-(3-phenanthryl)ethene and its ester derivative, respectively referred to as DPE-H and DPE-E, exhibited blue fluorescence. However, they underwent a two-step photoreaction sequence that yielded [7]helicenes, resulting in a gradual reduction of the fluorescence intensity. In contrast, the imide-fused derivative DPE-I displayed intense green fluorescence and it was unexpectedly photostable in solution, maintaining its highly efficient fluorescent nature even after prolonged light exposure. DPE-I, thus, provides a new type of highly efficient and robust diarylethene fluorophore.
@article{nose2025highly, title = {Highly emissive and robust diarylethene fluorophore incorporating imide-fused phenanthryl moieties}, author = {Nose, Keito and Yamaji, Minoru and Mori, Tadashi and Tani, Fumito and Goto, Kenta and Okamoto, Hideki}, journal = {Chem. Lett.}, volume = {54}, number = {5}, pages = {upaf091}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Oxford University Press UK}, doi = {10.1093/chemle/upaf091}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1093/chemle/upaf091}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {paper}, } -
 Inversion of circularly polarized luminescence by electric current flow during transitionAyumi Imayoshi*, Shinya Fujio, Yuuki Nagaya, Misato Sakai, Atsushi Terazawa, Misa Sakura, Keita Okada, Takahiro Kimoto, Tadashi Mori, Yoshitane Imai, Masahiko Hada, and Kazunori Tsubaki*Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2025, 27, 77–82.
Inversion of circularly polarized luminescence by electric current flow during transitionAyumi Imayoshi*, Shinya Fujio, Yuuki Nagaya, Misato Sakai, Atsushi Terazawa, Misa Sakura, Keita Okada, Takahiro Kimoto, Tadashi Mori, Yoshitane Imai, Masahiko Hada, and Kazunori Tsubaki*Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2025, 27, 77–82.The development of chiral compounds exhibiting circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) has advanced remarkably in recent years. Designing CPL-active compounds requires an understanding of the electric transition dipole moment (μ) and the magnetic transition dipole moment (m) in the excited state. However, while the direction and magnitude of μ can, to some extent, be visually inferred from chemical structures, m remains elusive, posing challenges for direct predictions based on structural information. This study utilized binaphthol, a prominent chiral scaffold, and achieved CPL-sign inversion by strategically varying the substitution positions of phenylethynyl (PE) groups on the binaphthyl backbone, while maintaining consistent axial chirality. Theoretical investigation revealed that the substitution position of PE groups significantly affects the orientation of m in the excited state, leading to CPL-sign inversion. Furthermore, we propose that this CPL-sign inversion results from a reversal in the rotation of instantaneous current flow during the S1 → S0 transition, which in turn alters the orientation of m. The current flow can be predicted from the chemical structure, allowing anticipation of the properties of m and, consequently, the characteristics of CPL. This insight provides a new perspective in designing CPL-active compounds, particularly for C2-symmetric molecules where the S1 -> S0 transition predominantly involves LUMO → HOMO transitions. If μ represents the directionality of electron movement during transitions, i.e., the “difference” in electron locations before and after transitions, then m could be represented as the “path” of electron movement based on the current flow during the transition.
@article{imayoshi2025inversion, title = {Inversion of circularly polarized luminescence by electric current flow during transition}, author = {Imayoshi, Ayumi and Fujio, Shinya and Nagaya, Yuuki and Sakai, Misato and Terazawa, Atsushi and Sakura, Misa and Okada, Keita and Kimoto, Takahiro and Mori, Tadashi and Imai, Yoshitane and Hada, Masahiko and Tsubaki, Kazunori}, journal = {Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.}, volume = {27}, number = {1}, pages = {77--82}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Royal Society of Chemistry}, doi = {10.1039/d4cp02968b}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1039/d4cp02968b}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {paper}, }