articles in 2020
all / 2026 / 2025 / 2024 / 2023 / 2022 / 2021 / 2020 / 2019 / 2018 / 2017 / 2016 / 2015 / 2014 / 2013 / 2012 / 2011 / 2010 / 2009 / 2008 / 2007 / 2006 / 2005 / 2004 / 2003 / 2002 / 2001 / 2000 / 1999 / 1998 / 1997 / 1996 / 1995 / 1994 / 1993
-
 Enhancing Photostability of a Coumarin Dye by Self-inclusion into a Cyclodextrin Cavity in Aqueous Solution and Living CellsHajime Shigemitsu*, Keigo Matsuda, Tadashi Mori, Hirotaka Nakatsuji, Michiya Matsusaki, and Toshiyuki Kida*Asian J. Org. Chem., 2020, 9, 2112–2115.
Enhancing Photostability of a Coumarin Dye by Self-inclusion into a Cyclodextrin Cavity in Aqueous Solution and Living CellsHajime Shigemitsu*, Keigo Matsuda, Tadashi Mori, Hirotaka Nakatsuji, Michiya Matsusaki, and Toshiyuki Kida*Asian J. Org. Chem., 2020, 9, 2112–2115.Photostable organic dyes are highly demanded for longtime or super-resolution bioimaging. Herein, we demonstrate effective improvement of photostability of a coumarin dye (Pacific Blue (PB)) by steric protection using a cyclodextrin. The PB conjugated cyclodextrin (PB−CD) showed 2.8 times higher photostability than PB ethyl amide (PB−EA) which is a comparative compound in vitro. The cyclodextrin conjugation to PB not only protect PB unit from reactive chemicals, but also suppress reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation which causes dye degradation. The effects afford significant improvement of photostability of PB dye. Finally, the photostability of PB−CD was evaluated using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) and the significant improvement effect was proofed even in living cells.
@article{shigemitsu2020enhancing, title = {Enhancing Photostability of a Coumarin Dye by Self-inclusion into a Cyclodextrin Cavity in Aqueous Solution and Living Cells}, author = {Shigemitsu, Hajime and Matsuda, Keigo and Mori, Tadashi and Nakatsuji, Hirotaka and Matsusaki, Michiya and Kida, Toshiyuki}, journal = {Asian J. Org. Chem.}, volume = {9}, issue = {12}, pages = {2112--2115}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Wiley Online Library}, doi = {10.1002/ajoc.202000365}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1002/ajoc.202000365}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {paper}, } -
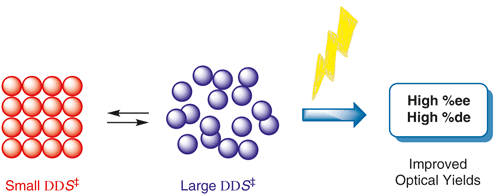 Relevance of the entropy factor in stereoselectivity control of asymmetric photoreactionsTadashi Mori*Synlett, 2020, 31, 1259–1267.
Relevance of the entropy factor in stereoselectivity control of asymmetric photoreactionsTadashi Mori*Synlett, 2020, 31, 1259–1267.Entropy as well as enthalpy factors play substantial roles in various chemical phenomena such as equilibrium and reactions. However, the entropy factors are frequently underestimated in most instances, particularly in synthetic chemistry. In reality, the entropy factor can be in competition with the enthalpy factor or can even be decisive in determining the overall free or activation energy change upon molecular interaction and chemical transformation, particularly where weak interactions in ground and/or excited states are significant. In this account, we overview the importance of the entropy factor in various chemical phenomena in both thermodynamics and kinetics and in the ground and excited states. It is immediately apparent that many diastereo- and enantioselective photoreactions are entropy-controlled. Recent advances on the entropy-control concept in asymmetric photoreactions are further discussed. Understanding the entropy-control concept will pave the way to improve, fine-tune, and even invert the chemo- and stereoselectivity of relevant chemical phenomena.
@article{mori2020relevance, title = {Relevance of the entropy factor in stereoselectivity control of asymmetric photoreactions}, author = {Mori, Tadashi}, journal = {Synlett}, volume = {31}, issue = {13}, pages = {1259--1267}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Georg Thieme Verlag}, doi = {10.1055/s-0040-1707962}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0040-1707962}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {review}, } -
 Enantiodifferentiating Photodimerization of a 2, 6-Disubstituted Anthracene Assisted by Supramolecular Double-Helix Formation with Chiral AminesAkio Urushima, Daisuke Taura, Makoto Tanaka, Naomichi Horimoto, Junki Tanabe, Naoki Ousaka, Tadashi Mori, and Eiji Yashima*Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 7478–7486.
Enantiodifferentiating Photodimerization of a 2, 6-Disubstituted Anthracene Assisted by Supramolecular Double-Helix Formation with Chiral AminesAkio Urushima, Daisuke Taura, Makoto Tanaka, Naomichi Horimoto, Junki Tanabe, Naoki Ousaka, Tadashi Mori, and Eiji Yashima*Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 7478–7486.A novel 2,6-anthrylene-linked bis(m-terphenylcarboxylic acid) strand (1) self-associates into a racemic double-helix. In the presence of chiral mono- and diamines, either a right- or left-handed double-helix was predominantly induced by chiral amines sandwiched between the carboxylic acid strands with accompanying stacking of the two prochiral anthracene linker units in an enantiotopic face-selective way, as revealed by circular dichroism and NMR spectral analyses. The photoirradiation of the optically active double helices complexed with chiral amines proceeded in a diastereo- (anti or syn) and enantiodifferentiating way to afford the chiral anti-photodimer with up to 98% enantiomeric excess when (R)-phenylethylamine was used as a chiral double-helix inducer. The resulting optically active anti-photodimer can recognize the chirality of amines and diastereoselectively complex with chiral amines.
@article{urushima2020enantiodifferentiating, title = {Enantiodifferentiating Photodimerization of a 2, 6-Disubstituted Anthracene Assisted by Supramolecular Double-Helix Formation with Chiral Amines}, author = {Urushima, Akio and Taura, Daisuke and Tanaka, Makoto and Horimoto, Naomichi and Tanabe, Junki and Ousaka, Naoki and Mori, Tadashi and Yashima, Eiji}, journal = {Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.}, volume = {59}, issue = {19}, pages = {7478--7486}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Wiley Online Library}, doi = {10.1002/anie.201916103}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201916103}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {paper}, } -
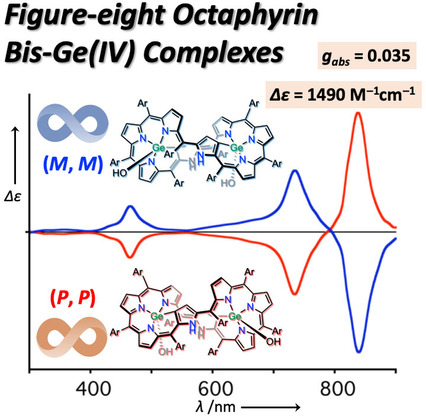 Figure-eight Octaphyrin Bis-Ge (IV) Complexes: Synthesis, Structures, Aromaticity, and Chiroptical PropertiesMondo Izawa, Taisuke Suito, Shin-ichiro Ishida, Daiki Shimizu, Takayuki Tanaka*, Tadashi Mori*, and Atsuhiro Osuka*Chem. Asian J., 2020, 15, 1440–1448.
Figure-eight Octaphyrin Bis-Ge (IV) Complexes: Synthesis, Structures, Aromaticity, and Chiroptical PropertiesMondo Izawa, Taisuke Suito, Shin-ichiro Ishida, Daiki Shimizu, Takayuki Tanaka*, Tadashi Mori*, and Atsuhiro Osuka*Chem. Asian J., 2020, 15, 1440–1448.Highly twisted structures of expanded porphyrin provide a prominent basis to unravel the relationship between aromaticity and chirality. Here we report the synthesis of bis-Ge(IV) complexes of [38]octaphyrin that display rigid figure-eight structures. Two bis-Ge(IV) [38]octaphyrin isomers with respect to the stereochemistry of the axial hydroxy groups on the germanium ions were obtained and found to be aromatic. Upon oxidation with MnO2, these [38]octaphyrin complexes were converted to a single syn-type isomer of [36]octaphyrin with retained figure-eight conformation. The enantiomers have been successfully separated by HPLC equipped with a chiral stationary phase. While aromatic [38]octaphyrin Ge(IV) complexes showed quite large molar circular dichroism of up to Δϵ=1500 M−1cm−1 with a dissymmetry factor gabs of 0.035, weakly antiaromatic [36]octaphyrin Ge(IV) complexes underscored moderate values; Δϵ=540 M−1cm−1 with gabs of 0.023. Thus, the figure-eight octaphyrin scaffold has been proved to be an attractive platform for novel chiroptical materials with tunable aromaticity.
@article{izawa2020figure, title = {Figure-eight Octaphyrin Bis-Ge (IV) Complexes: Synthesis, Structures, Aromaticity, and Chiroptical Properties}, author = {Izawa, Mondo and Suito, Taisuke and Ishida, Shin-ichiro and Shimizu, Daiki and Tanaka, Takayuki and Mori, Tadashi and Osuka, Atsuhiro}, journal = {Chem. Asian J.}, volume = {15}, issue = {9}, pages = {1440--1448}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Wiley Online Library}, doi = {10.1002/asia.202000159}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.202000159}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {paper}, } -
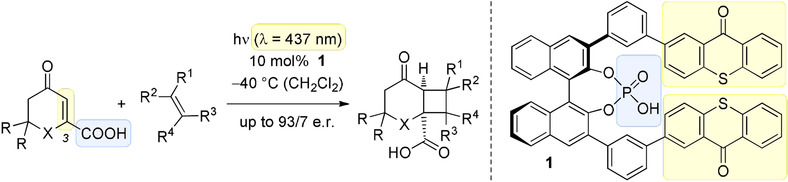 A thioxanthone sensitizer with a chiral phosphoric acid binding site: properties and applications in visible light-mediated cycloadditionsFranziska Pecho, You-Quan Zou, Johannes Gramüller, Tadashi Mori, Stefan M Huber, Andreas Bauer, Ruth M Gschwind, and Thorsten Bach*Chem. Eur. J., 2020, 26, 5190–5194.
A thioxanthone sensitizer with a chiral phosphoric acid binding site: properties and applications in visible light-mediated cycloadditionsFranziska Pecho, You-Quan Zou, Johannes Gramüller, Tadashi Mori, Stefan M Huber, Andreas Bauer, Ruth M Gschwind, and Thorsten Bach*Chem. Eur. J., 2020, 26, 5190–5194.A chiral phosphoric acid with a 2,2’-binaphthol core was prepared that displays two thioxanthone moieties at the 3,3’-position as light-harvesting antennas. Despite its relatively low triplet energy, the phosphoric acid was found to be an efficient catalyst for the enantioselective intermolecular [2+2] photocycloaddition of β-carboxyl-substituted cyclic enones (e.r. up to 93:7). Binding of the carboxylic acid to the sensitizer is suggested by NMR studies and by DFT calculations to occur by means of two hydrogen bonds. The binding event not only enables an enantioface differentiation but also modulates the triplet energy of the substrates.
@article{pecho2020thioxanthone, title = {A thioxanthone sensitizer with a chiral phosphoric acid binding site: properties and applications in visible light-mediated cycloadditions}, author = {Pecho, Franziska and Zou, You-Quan and Gramüller, Johannes and Mori, Tadashi and Huber, Stefan M and Bauer, Andreas and Gschwind, Ruth M and Bach, Thorsten}, journal = {Chem. Eur. J.}, volume = {26}, issue = {23}, pages = {5190--5194}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Wiley Online Library}, doi = {10.1002/chem.202000720}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202000720}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {paper}, } -
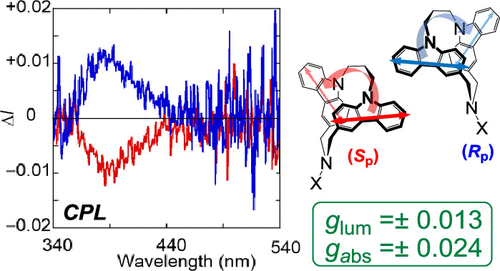 Combined Experimental and Theoretical Studies on Planar Chirality of Partially Overlapped C2-Symmetric [3.3](3,9)DicarbazolophanesKeita Tani*, Kanae Imafuku, Miyuki Eiraku Masaki, Haruka Kato, Kazushige Hori, Koji Kubono, Masatsugu Taneda, Takunori Harada, Kenta Goto, Fumito Tani, and Tadashi Mori*J. Phys. Chem. A, 2020, 124, 2057–2063.
Combined Experimental and Theoretical Studies on Planar Chirality of Partially Overlapped C2-Symmetric [3.3](3,9)DicarbazolophanesKeita Tani*, Kanae Imafuku, Miyuki Eiraku Masaki, Haruka Kato, Kazushige Hori, Koji Kubono, Masatsugu Taneda, Takunori Harada, Kenta Goto, Fumito Tani, and Tadashi Mori*J. Phys. Chem. A, 2020, 124, 2057–2063.Partially overlapped dicarbazolophanes exhibit a planar chirality. In this study, C2-symmetrical [3.3](3,9)dicarbazolophane derivatives (CZ1–CZ3) have been optically resolved by preparative chiral high-performance liquid chromatography for the first time. In their circular dichroism (CD) spectra, moderate Cotton effects (CEs) were observed for their 1Lb and 1La transitions (|Δε| = 10–12 and 51–57 M–1 cm–1, respectively), while intense CEs were notified in their 1B transitions (|Δε| = 156–216 M–1 cm–1), absorption dissymmetry (gabs) factors being in orders of 10–2. Circularly polarized luminescence spectrum was also obtained for cyanamide derivative CZ1, with a comparative luminescence dissymmetry (glum) factor of 0.013. A computational investigation was applied to address the factors for such remarkable chiroptical responses in these dicarbazolophanes of planar chirality. Absolute configurations were unambiguously determined by the comparison of experimental and theoretical CD spectra, which was affirmed by the X-ray crystal structural analysis of enantiomerically pure sulfonamide derivative CZ2.
@article{tani2020combined, title = {Combined Experimental and Theoretical Studies on Planar Chirality of Partially Overlapped C2-Symmetric [3.3](3,9)Dicarbazolophanes}, author = {Tani, Keita and Imafuku, Kanae and Masaki, Miyuki Eiraku and Kato, Haruka and Hori, Kazushige and Kubono, Koji and Taneda, Masatsugu and Harada, Takunori and Goto, Kenta and Tani, Fumito and Mori, Tadashi}, journal = {J. Phys. Chem. A}, volume = {124}, issue = {10}, pages = {2057--2063}, year = {2020}, publisher = {ACS Publications}, doi = {10.1021/acs.jpca.0c00286}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.0c00286}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {paper}, } -
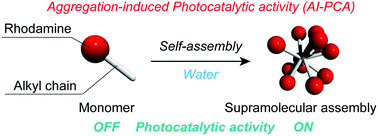 Aggregation-induced photocatalytic activity and efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution of amphiphilic rhodamines in waterHajime Shigemitsu*, Youhei Tani, Tomoe Tamemoto, Tadashi Mori, Xinxi Li, Yasuko Osakada, Mamoru Fujitsuka, and Toshiyuki Kida*Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 11843–11848.
Aggregation-induced photocatalytic activity and efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution of amphiphilic rhodamines in waterHajime Shigemitsu*, Youhei Tani, Tomoe Tamemoto, Tadashi Mori, Xinxi Li, Yasuko Osakada, Mamoru Fujitsuka, and Toshiyuki Kida*Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 11843–11848.The development of photocatalysts is an essential task for clean energy generation and establishing a sustainable society. This paper describes the aggregation-induced photocatalytic activity (AI-PCA) of amphiphilic rhodamines and photocatalytic functions of the supramolecular assemblies. The supramolecular assemblies consisting of amphiphilic rhodamines with octadecyl alkyl chains exhibited significant photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation in water, while the corresponding monomeric rhodamines did not exhibit photocatalytic activity. The studies on the photocatalytic mechanism by spectroscopic and microscopic analyses clearly demonstrated the AI-PCA of the rhodamines. Moreover, the supramolecular assemblies of the rhodamines exhibited excellent photocatalytic hydrogen evolution rates (up to 5.9 mmol g−1 h−1).
@article{shigemitsu2020aggregation, title = {Aggregation-induced photocatalytic activity and efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution of amphiphilic rhodamines in water}, author = {Shigemitsu, Hajime and Tani, Youhei and Tamemoto, Tomoe and Mori, Tadashi and Li, Xinxi and Osakada, Yasuko and Fujitsuka, Mamoru and Kida, Toshiyuki}, journal = {Chem. Sci.}, volume = {11}, issue = {43}, pages = {11843--11848}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Royal Society of Chemistry}, doi = {10.1039/d0sc04285d}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1039/d0sc04285d}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {paper}, } -
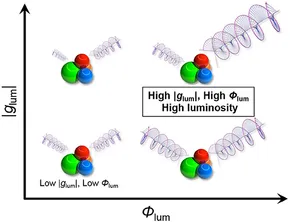 Irreverent nature of dissymmetry factor and quantum yield in circularly polarized luminescence of small organic moleculesYuya Nagata and Tadashi Mori*Front. Chem., 2020, 8, 448.
Irreverent nature of dissymmetry factor and quantum yield in circularly polarized luminescence of small organic moleculesYuya Nagata and Tadashi Mori*Front. Chem., 2020, 8, 448.Recently, a rational modification of small organic molecules has attracted considerable attention for designing advanced materials with enhanced circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) activity. A particular emphasis has been placed on fully allowed π-π* transition of rigid aromatic systems, due to their relatively superior emission properties or quantum yields of luminescence (Φlum). However, their dissymmetry factors (glum), differential left and right CPL intensities, are typically disappointingly low at least in one to two orders of magnitude. Truly useful organic CPL materials, rated by a circular polarization luminosity index (ΛCPL) per single molecule, possess both |glum| and Φlum values high. However, how to improve these two factors simultaneously with a proper molecular design is an open question. Here, we addressed this issue by theoretical and statistical inspection on a possible relation of the glum and Φlum values. According to the analysis, we propose simple, unpretentious, yet pertinent guidelines for designing superior organic CPL materials for the future with large ΛCPL values.
@article{nagata2020irreverent, title = {Irreverent nature of dissymmetry factor and quantum yield in circularly polarized luminescence of small organic molecules}, author = {Nagata, Yuya and Mori, Tadashi}, journal = {Front. Chem.}, volume = {8}, pages = {448}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Frontiers Media SA}, doi = {10.3389/fchem.2020.00448}, url = {https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00448}, dimensions = {true}, tab = {review}, }